When setting up industrial automation or SCADA systems, one of the first communication choices you’ll face is Modbus RTU vs Modbus TCP. Both are based on the Modbus protocol, a widely used open standard for communication between programmable logic controllers (PLCs), sensors, and other field devices.
However, while both share the same command structure, they differ significantly in communication media, speed, scalability, and integration capabilities.
In this guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know to choose the right Modbus version for your system.
Article Content
What Is Modbus?
Modbus is a serial communication protocol originally developed by Modicon (now Schneider Electric) in 1979. It allows master and slave devices to exchange data — for example, a PLC (master) reading data from temperature sensors (slaves).
Over time, Modbus has evolved into several variants to meet new communication technologies:
- Modbus RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) — serial communication
- Modbus ASCII — text-based serial version
- Modbus TCP/IP — Ethernet-based communication
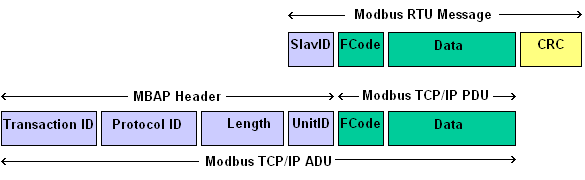
What Is Modbus RTU?
Modbus RTU is the traditional form of Modbus communication, running over RS-232 or RS-485 serial lines. It uses a binary encoding format for compact and efficient data exchange.
Key Characteristics
- Communication via RS-485 or RS-232
- Master/Slave architecture
- Compact binary frame format
- Uses CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check) for error detection
- Ideal for short-distance, noise-resistant environments
Advantages
- Simple and cost-effective
- Reliable for small, localized networks
- Low hardware requirements
- Excellent for legacy industrial systems
Limitations
- Slower data transfer speeds (up to 115.2 kbps)
- Limited device count per segment (typically 32)
- Difficult to scale over long distances
What Is Modbus TCP?
Modbus TCP (or Modbus over TCP/IP) is the modern version of Modbus that runs over Ethernet networks. It encapsulates the Modbus protocol within TCP/IP packets, enabling communication over LAN, WAN, and even the internet.
Key Characteristics
- Communication via Ethernet (Cat5e/Cat6)
- Uses TCP/IP protocol stack
- Client/Server architecture instead of Master/Slave
- No need for slave IDs — uses IP addresses instead
Advantages
- High-speed communication (up to 100 Mbps or more)
- Easy integration with IT networks, SCADA, and IoT systems
- Supports hundreds of devices
- Built-in error handling and reliability from TCP/IP
Limitations
- Slightly higher setup cost
- Requires Ethernet infrastructure
- May need additional cybersecurity measures
Modbus RTU vs Modbus TCP: Comparison Table
| Feature | Modbus RTU | Modbus TCP |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Serial (RS-485/RS-232) | Ethernet |
| Speed | Up to 115.2 kbps | Up to 100 Mbps+ |
| Topology | Bus/Daisy Chain | Star/Ethernet Network |
| Addressing | Slave ID (1–247) | IP Address |
| Error Checking | CRC | TCP/IP Built-in |
| Scalability | Limited | Highly scalable |
| Integration | Difficult with IT/IoT | Easy integration |
| Cost | Lower | Slightly higher |
| Best For | Legacy, isolated systems | Modern, networked systems |
Which One Should You Choose?
Choosing between Modbus RTU and Modbus TCP depends on your specific application:
| Application Scenario | Recommended Protocol |
|---|---|
| Small local control systems | Modbus RTU |
| Long cable runs, low-speed data | Modbus RTU |
| Large-scale industrial automation | Modbus TCP |
| Integration with SCADA or cloud | Modbus TCP |
| High-speed, real-time monitoring | Modbus TCP |
If you’re upgrading from an older RTU system, many devices and gateways support Modbus RTU-to-TCP conversion, allowing hybrid setups that combine both protocols seamlessly.
How to Integrate Modbus RTU and TCP
Many industries use Modbus gateways or converters to bridge the two communication types.
For example:
- Modbus RTU to TCP gateways connect serial devices to Ethernet networks.
- Protocol converters translate data frames automatically.
This allows you to maintain existing RTU devices while adding modern TCP-based controllers or HMIs.
Final Thoughts
Both Modbus RTU and Modbus TCP remain powerful, reliable standards in industrial automation.
- Choose Modbus RTU for simple, local, cost-efficient applications.
- Choose Modbus TCP for scalable, high-speed, and networked systems.
Understanding these differences ensures your automation infrastructure remains robust, future-proof, and compatible with modern Industry 4.0 solutions.
