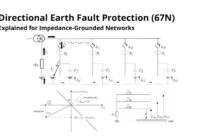
Directional Earth Fault Protection (67N) Explained for Impedance-Grounded Networks
This article focuses specifically on directional earth fault protection (ANSI 67N) for electrical networks with an impedance-grounded neutral. We’ll be releasing more articles soon that explore how directional earth protection behaves in other grounding systems. The goal is to give you a complete, system-by-system view of how earth fault protection works. Stay tuned—there’s much more coming. In this… Read More »